Research & Discovery
Research & Discovery
A Blog Devoted to UD Innovation, Excellence and Scholarship
Research & Discovery
A Blog Devoted to UD Innovation, Excellence and Scholarship
Greener hydrogen from water
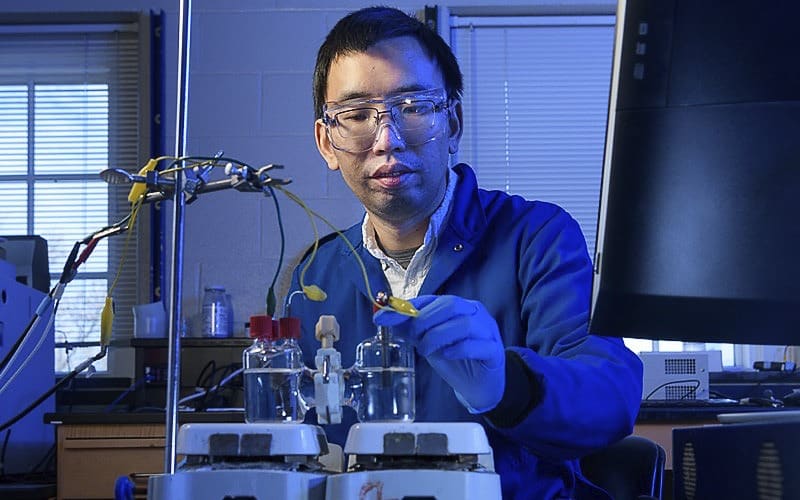
ABOVE: Feng Jiao, an associate professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and associate director of the Center for Catalytic Science and Technology at UD, in his lab. | Photo by Kathy F. Atkinson
UD innovator explores catalysts that pull their weight and serve the environment
The idea of using hydrogen as the basis of a clean sustainable energy source, often termed a hydrogen economy, has been a topic of conversation for decades. Hydrogen fuel, for example, doesn’t emit any carbon dioxide and is considered more sustainable than traditional fossil fuels.
The lightest element on the periodic table, hydrogen is an energy carrier that can be used to power fuel cells in transportation vehicles, buildings or other infrastructure. Hydrogen also can help upcycle things like straw, grasses and other biomass into high-value chemicals used in everything from plastics to paint to personal care items.
But the technology driving these innovations has faced serious challenges, chiefly because freeing hydrogen for these uses is produced mainly through processes that require fossil fuels and come with an environmental cost — carbon dioxide.
Now, University of Delaware engineer Feng Jiao has patented a process that may hold the key to producing greener hydrogen from water using electricity and a copper-titanium catalyst.